背景介绍
GhostNet:来自华为诺亚方舟实验室,于2020年被CVPR接受,借鉴了大量优秀神经网络的特点,提出了一种新型的神经网络架构。
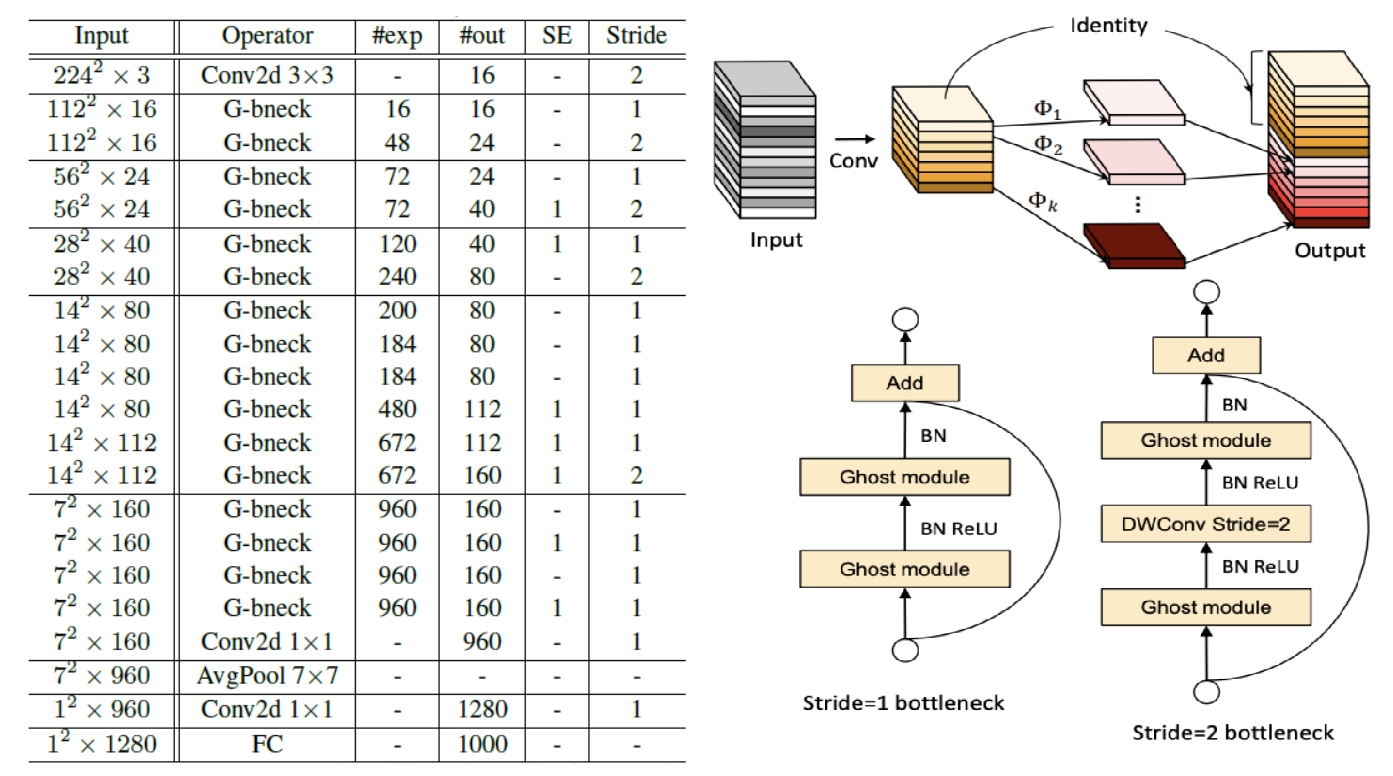
GhostNet特点
在Ghost Module中引入瓶颈结构和GroupConv分组卷积
在Ghost Bottleneck中引入DepthwiseConv深度可分离卷积和Squeeze-and-Excitation模块
Group Convolution
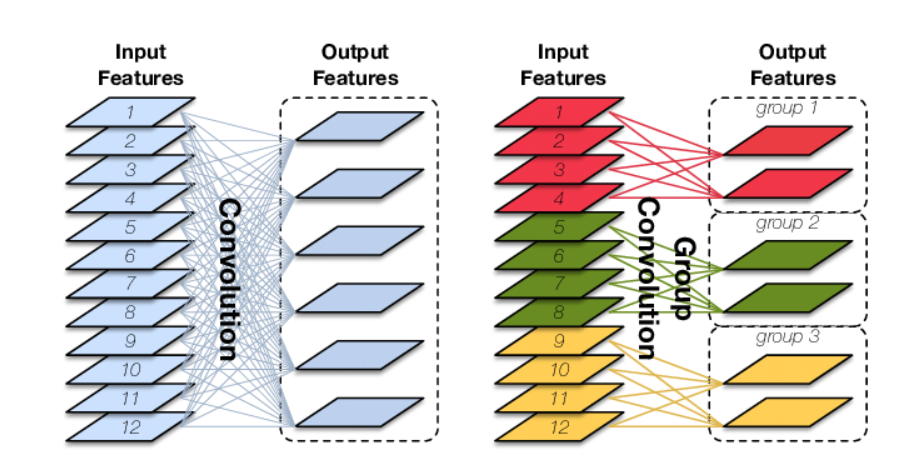
Group Convolution(分组卷积):传统卷积是采用一种卷积全连接的思想,特征图中的每一个像素点都结合了图像中所有通道的信息。而分组卷积特征图像每一个像素点只利用到一部分原始图像的通道。
主要作用是大大降低网络的参数量。如果一个64x64x256的图像,经过5x5的卷积核后变为64x64x256的图像,经过普通卷积的参数量为256x(256x5x5+1)=1638656,而分成32组的分组卷积的参数量为256x(8*5x5+1)=51456,参数量缩小了约32倍,当组数变成通道数时,则类似于Depthwise Convolution深度卷积
Depthwise Convolution
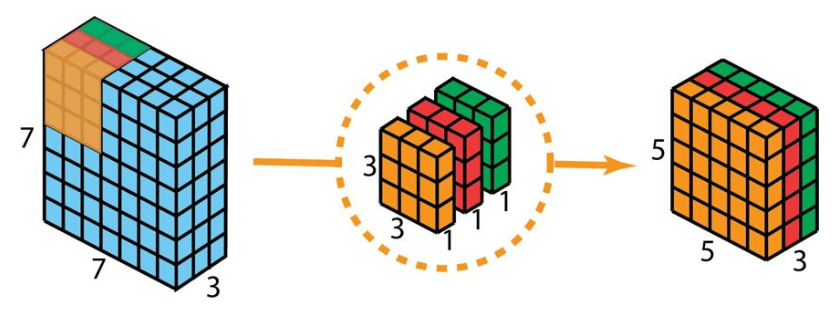
Depthwise Convolution(深度卷积):在每一个通道上单独进行卷积**
参数depth_multiplier默认为1,代表每个通道数进行一次单独卷积,输出的通道数和输入通道数相等,设置depth_multiplier=n,则代表每个通道数进行n次单独卷积,输出通道数是输入通道数的n倍。
主要作用是大大降低网络的参数量。如果一个8x8x1024的特征图,经过5x5的卷积核后变为8x8x1024的图像,经过普通卷积的参数量为1024x(1024x5x5+1)=26215424,而深度卷积参数量为1024x(1x5x5+1)=26624,参数量缩小了约1024倍。
Squeeze-and-Excitation
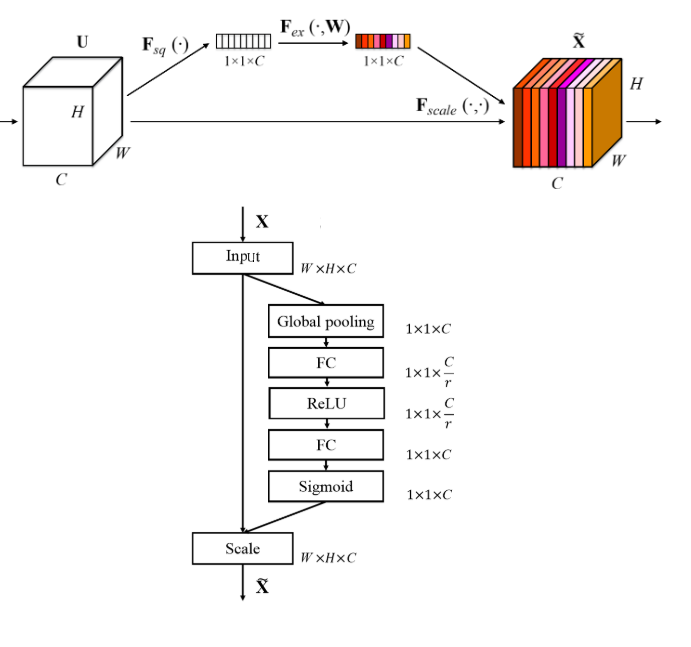
Squeeze-and-Excitation:又称为特征重标定卷积,或者注意力机制。具体来说,就是通过学习的方式来自动获取到每个特征通道的重要程度,然后依照这个重要程度去提升有用的特征并抑制对当前任务用处不大的特征。
首先是 Squeeze操作,先进行全局池化,具有全局的感受野,并且输出的维度和输入的特征通道数相匹配,它表征着在特征通道上响应的全局分布。
然后是Excitation操作,通过全连接层为每个特征通道生成权重,建立通道间的相关性,输出的权重看做是进过特征选择后的每个特征通道的重要性,然后通过乘法逐通道加权到先前的特征上,完成在通道维度上的对原始特征的重标定。
GhostNet图像分析

TensorFlow2.0实现
1 | from functools import reduce |
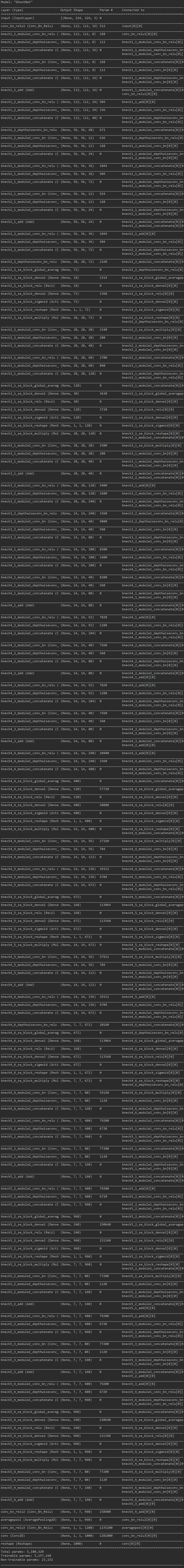
GhostNet小结
GhostNet是一种复杂的轻量级深度学习网络,参数量为5M,其借鉴了大量优秀的深度学习网络的精髓,如MobileNet的深度可分离卷积思想,AlexNet的分组卷积思想,SENet的注意力机制,因此获得了较好的效果。