
定义
迭代器模式(Iterator):属于行为型模式,可以让使用者在不暴露集合底层表现形式的情况下,遍历集合中的所有元素。
代码实战
1 | interface MyIterator<T> { |
类图
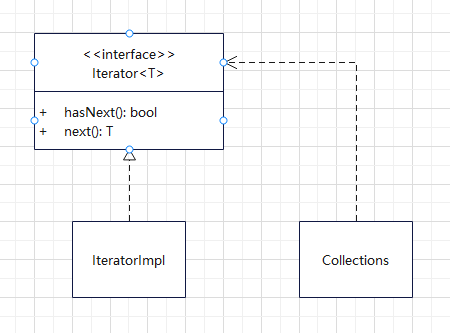
特点
迭代器模式的特点是,创建一个迭代器接口,其中包含hasNext方法和next方法。hasNext方法用于判断是否遍历结束,next方法是返回下一个元素。
使用者自定义一个集合类,并定义一个迭代器接口的实现类,在这个next方法中按照某个特定顺序遍历元素。集合类提供一个iterator方法,用于获取迭代器对象。
总结
迭代器模式遇到的场景非常多,但是使用场景比较少,主要是在各种语言的集合库中,往往都提供了使用迭代器访问集合的方法。